Course Outline
· Basic concepts: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, One-tailed
and two-tailed tests, Type I and Type II
errors, Level of significance, Critical region, Value, Test statistics, Steps
in hypothesis testing.
· Z-test: Difference between two means of large samples with
unknown population variance.
· T-test: Difference between two means of small samples with
unknown common variance.
· Chi-square test: Significance test of independence.
· Significance test for correlation coefficient.
Introduction
· Hypothesis: On
the basis of sample information, we make certain decisions about the
population. In making such decision, we make certain assumptions. These
assumptions are known as statistical hypothesis. These hypothesis are tested.
Assuming the hypothesis correct we calculate the probability of getting the
observed sample. If this probability is less than a certain assigned value, the
hypothesis is to be rejected.
· Null hypothesis: Null
hypothesis is the hypothesis of no difference. The null hypothesis asserts that
there is no difference between the statistic and the population parameter and
whatever observed difference is there is merely due to fluctuations in sampling
from the same population. Null hypothesis is usually denoted by the symbol H0.
· Alternative hypothesis: Rejecting
null hypothesis implies that it is rejected in favour of some other hypothesis
which is accepted when H0 is rejected is called alternative
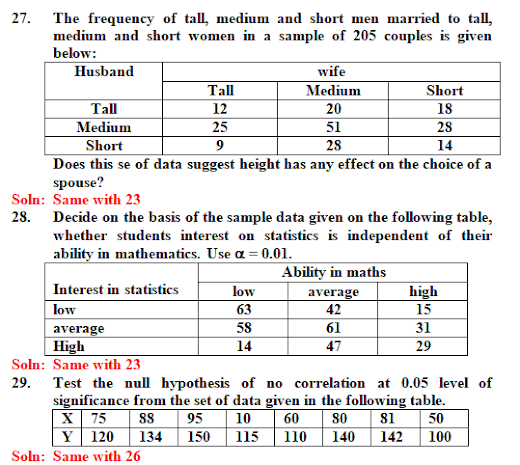
hypothesis and is represented by H1. Alternative hypothesis can be
two sided or one sided. The alternative hypothesis represents the conclusion
that would be reached if there were sufficient evidence from sample information
to decide that the null hypothesis is unlikely to be true and we can therefore
reject it.
Example:
The null hypothesis is H0: m = m0 and
Alternative hypothesis may be
i) H1 : m ¹ m0 (i.e. m > m0 or m < m0) (Two tailed)
ii) H1 : m > m0 (right
tailed)
iii) H1 : m < m0 (left
tailed)

21. In a random sample, 74 of
250 persons who watched a certain television program in black and white and 92
of 250 person who watch the same program in coloured remembered 2 hours letter
what product were advertised. Use chi-square statistics to test the null
hypothesis q1 = q2 against the
alternative hypothesis q1 ¹ q2 at the 0.01 level of significance.
Soln: As in Q. No. 10





















0 Comments