Objective Questions
1. Which of the following is not true?
a. Every closed sphere is a closed set.
b. Every closed interval is a closed set.
c. Every finite subset of a metric space is closed.
d. Every open sphere is a closed set.
2. A subset A of a metric space (X, d)
is said to be closed if:
a. A contains all its limit points
b. A contains all adherent points
c. A contains all interior points
d. A is a neighbourhood of its points
3. A
subject A of a compact metric space (X, d) is itself compact if and only if:
a. it
is open in (X, d) b. it is
closed in (X, d)
c. it is compact in (X, d) d. it is bounded in (X, d)
4. Which
of the following is not a true statement?
a. Every closed sphere is a closed set
b. Every open sphere is a open set
c. The empty set f and the whole space X are closed sets in (X, d)
d. The
empty f set and the whole space X are
open sets in (X, d)
5. Let
X is any set and Á is a
collection of subjects of X is said to be a topology if
a. f, x Î Á
b. The union of an arbitrary family of sets in Á is a member of Á
c. The intersection of finite number of set in Á is a member of Á
d. above
of all
6. Let
(X, d1) and (Y, d2) be any two metric spaces then f:X ® Y is continuous if and only if
a. f - 1(G) is closed in X, wherever G is open in Y
b. f - 1(G) is open in X,
wherever G is open in Y
c. f - 1(G) is open in X, wherever G is closed Y
d. f - 1(G) is closed in X, wherever G is intersected in Y
7. Let
X be a non-empty set, which of the following is not the necessary condition for
the metric d: X ´ X ® R?
a. d(x, y) ³ 0 " x, y ÎX
b. d(x, y) = d(y, x) " x, y ÎX
c. d(x,
z) ³ d(x, y) + d(y, z) " x, y, z Î R
d. d(x, y) £ d (x, y) + d(y, z) " x, y, z Î X
8. If
R¥ be extended to set
of real numbers on which a matrix d is defined by d(x, y) = |f(x) - f(y)| "
x, y, z Î R¥
then the matrix space (R¥,
d) is
a. bounded b. unbounded
c. R¥ does not exist d. R¥ is not a matrix space
9. In
any metric space (X, d) which of the following is not true?
a. The union of an arbitrary family of open set is open
b. The intersection of a finite number of open sets is open
c. The intersection of an arbitrary family of closed set is closed
d. The
union of an arbitrary family of closed sets is closed
10. Which
one of the following set is open in the metric subspace [0, 1] of the Euclidean
metric space Â1?
a. [0, 1/2] b.(1/3, 1/2] c. (1/3, 1/2) d. all of the above
11. Which
one of the following collection is an open covering of the real line Â?
a. {n, n + 1}: nÎ Z+ b.
{(n, n + 1): n Î Z
c. {(n, n + 2): n Î Z d. none of the above
12. Which
of the following is not true?
a. d(x1,
x2) = (x1 - x2) b.
|x1 + x2| £ |x1| + |x2|
c. d(x1, y1) £ d(x1, z1) + d(z1, y1) d. none of the above
13. Which
of the following is an open set?
a. the empty set b. open sphere
c. the entire space d. all of the above
14. Which
of the following is not a closed set with metric space (X, d)?
a. the empty b. the whole space
c. the set of rational numbers d. the set of natural numbers
15. If A and B be any two subjects of a metric
space (X, d) then which one of the following is not true?
16. In a metric space, which of the following is true?
a. Every open sphere S(x) is open
b. The union of any number of open set is open
c. The intersection of any number of closed set is closed
d. All of the above
17. Which
set of the following contains all its limit points?
a. {0, 1, 1/2, 1/3, …} b. [a, b] c. [a, b] d. (a, b)
18. Which one of the following is not an open covering of the real
line Â?
a. {(- n, n): n Î Z+} b. {(n, n + 2): n Î Z+}
c. {(a, b) : a, b Î Â} d.{(n, n + 1): n Î Z+}
19. Which one of the following set is compact?
a. (0, 1) b. (0, 1) c.[0, 1] d. Â
20. Which
of the following is true ?
a. Every open sphere is an open set.
b. The empty set and f is open set.
c. The whole space X with any metric is open set.
d. All of
above
21. In
any metric space (X, d), which of the following is not true?
a. The union of arbitrary family of open sets is open
b. The intersection of a finite number of open sets is open
c. The
intersection of arbitrary family of open sets is open
d. The intersection of arbitrary family of closed sets is closed
22. In
any metric space (X, d), which of the following is not true?
a.
The union of arbitrary family of closed sets is closed
b. The intersection of an arbitrary family of closed sets is closed
c. The intersection of arbitrary family of open sets is open
d. The union of finite number of closed sets is closed
25. Let A and B are any subsets of metric space
(X, d), then which of the following is true ?
a. is closed
b. A = is and only if A is closed
c is the smallest closed super set of A
d. All of
above
24. Which
of the following is true ?
a. The canter set is a perfect set
b. The cantor set is nowhere dense
c. The Euclidean space is Rn separable
d. All of
above
25. Which
of the following is false ?
a. Every closed subset of a compact metric space is compact.
b. Any closed interval with the usual metric is compact
c. Every compact subset F of a metric space (X, d) is closed.
d. Every
compact subset A of a metric space (X, d) is unbounded.
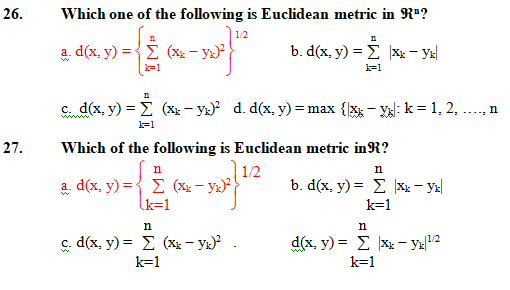

0 Comments